Disulfiram is an FDA-approved drug that has been in use for over 50 years. Its approved indication is as an alcohol antagonist to help alcoholic patients stay sober. Disulfiram is now being used and researched for the treatment of Lyme disease. Lyme disease is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria, Borrelia burgdorferi. The bacteria is transmitted when an infected black-legged tick, also known as deer tick, bites humans. Recent research has found that disulfiram has been shown to have potent antibacterial properties. Compounding Disulfiram for Lyme Disease is now being researched and studied across the world.
What is Disulfiram and how does it work?
Disulfiram inhibits the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase which leads to a buildup of acetaldehyde. As Dr Kinderlehrer MD explains on lymedisease.org, this buildup of acetaldehyde may be why disulfiram exhibits antibacterial effects, but the exact mechanism is still unclear. Studies have demonstrated Disulfiram’s antibacterial action against several different strains of bacteria as well as the Malaria parasite.
Number one against Borrelia burgdorferi.
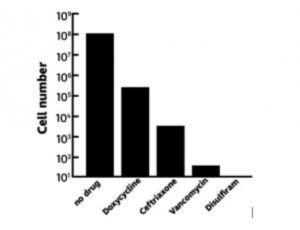
In 2016, researchers at Stanford reported on new drug candidates against Borrelia burgdorferi using a technique known as high-throughput screening. They ranked disulfiram as number one in activity against Borrelia burgdorferi among their top 20 hits. The researchers compared the activity of disulfiram against a few other well-known drugs used in the treatment of Lyme disease.
This bar graph depicts the number of colonies remaining after treating Borrelia burgdorferi with the following four drugs: doxycycline, ceftriaxone, vancomycin, and disulfiram. It is clear that vancomycin is a powerful drug to treat Lyme disease. But disulfiram completely sterilized the culture.
Since disulfiram has been shown to kill Plasmodium falciparum (malaria) in the laboratory, it is not surprising that it would also be effective against Babesia. Dr. Lewis is planning to do a study on mice infected with Bb. In addition, Dr. Brian Fallon at Columbia University has announced his intention to undertake a controlled trial using disulfiram in well-characterized patients with Lyme disease.
How Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy Can Help
Disulfiram doses used for treating Lyme are generally lower than those used for treating alcohol dependency. This is where a PCAB accredited compounding pharmacy such as Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy can help. For Lyme, doses may start as low as 25mg every 3 days and be titrated up to a maximum of 500mg daily based on how well the patient tolerates the drug. Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy can share recent research articles with your physician to assist them in determining an appropriate dose for each individual patient. Pavilion’s team of clinical pharmacists can compound disulfiram in a dye free, lactose free, acid resistant capsule. The disulfiram powder we use in our lab is USP grade, third party tested (purity, potency, heavy metals, etc.), and is supplied from a FDA registered manufacturer.
There are several known side effects and drug interactions of disulfiram that your doctor will describe when deciding if this medication is right for you. It is very important to avoid alcohol intake and also try to avoid yeast while on this treatment
Low Dose Naltrexone ( LDN ) may also be beneficial for patients with Lyme Disease. See our blog post for more information about LDN.
Contact Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy today via our online chat, email, or telephone with any questions relating to Compounding Disulfiram for Lyme Disease.
ph: 404-350-5780
fax: 404-350-5640
References
1.Long TE. Repurposing Thiram and Disulfiram as Antibacterial Agents for Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(9):e00898-17
2.Scheibel LW, Adler A, Trager W. Tetraethylthiuram disulfide (Antabuse) inhibits the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979;76(10):5303-7.
3. Pothineni VR, Wagh D, Babar MM, et al. Identification of new drug candidates against Borrelia burgdorferi using high-throughput screening. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:1307-22.
4. Liegner KB. Disulfiram (Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide) in the Treatment of Lyme Disease and Babesiosis: Report of Experience in Three Cases. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 May 30;8(2). pii: E72. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8020072.
5. https://www.lymedisease.org/disulfiram-kinderlehrer/#_edn3 accessed 4 19, 2020