Are you taking thyroid replacement hormones? A compounding pharmacy can help you get more out of your treatment plan. Thyroid hormone therapy involves the use of manmade hormones to raise abnormally low thyroid levels. This type of treatment is of special benefit for people with hypothyroidism or other types of thyroid disease. Learn more about how compounding pharmacies can aid in thyroid hormone replacement therapy below.
About Thyroid Hormones
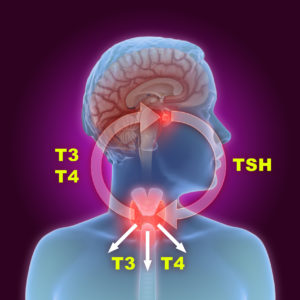
A butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, known as the thyroid, produces thyroid hormones. Specifically, the thyroid gland sits towards the front of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple.
The thyroid gland is an important part of the endocrine system. Hormones are “chemical messengers” that tell cells and tissue in various parts of the body how to function. Thyroid hormones help regulate the body’s metabolic rate, which is the rate at which the body converts food into energy. The metabolic rate also affects how fast your heart beats, the amount of heat your body produces, and even how quickly you can think. Furthermore, thyroid hormones also help regulate the heart and digestive function, muscle control, brain development, mood, and bone maintenance. In other words, these thyroid hormones dictate how well your body uses energy.
To function well, the thyroid requires a steady supply of iodine. In a complex process that involves other organs and glands, the thyroid also relies on other hormones to tell it when to produce hormones. Specifically, the brain releases a hormone that tells the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH), which stimulates hormone production in the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland produces two hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Both T3 and T4 control your metabolism.
The thyroid should produce the right amount of T3 and T4 hormones for normal body function. Sometimes the gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone, however, in a condition known as hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Hoarse voice
- Dry skin
- Puffy face
- Muscle aches
- Stiff joints
- Heavy or abnormal menstrual periods
- Thinning hair
- Slow pulse
- Depression
- Impaired memory
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
Some people are at a higher risk of hypothyroidism. You are at a higher risk of hypothyroidism if you are a woman, over the age of 60, have a family history of the disease, or if you have an autoimmune disease. Your risk for hypothyroidism is also higher if have received treatment with anti-thyroid medications or radioactive iodine, received radiation to your neck or upper chest, or have had thyroid surgery.
Other diseases can affect the thyroid gland, such as:
Hyperthyroidism – The gland secretes excessive amounts of thyroid hormones; may cause weight loss and other symptoms
Goiter – Enlargement of the thyroid gland
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid nodules – Lumps on the thyroid gland
Thyroiditis – Inflammation of the thyroid gland
Hashimoto’s disease – Autoimmune disease that destroys the thyroid gland to cause hormonal imbalance
Treatment of Thyroid Conditions Using Thyroid Hormone Replacement
Doctors treat hypothyroidism and other thyroid conditions with thyroid hormone replacements, specifically T3 and T4.
T3 is more active than is T4, but doctors typically prescribe synthetic T4 for patients with hypothyroidism. This is because the body turns natural thyroid hormones or synthetic T4 into T3 in the bloodstream. When T4 molecules contact other cells in the bloodstream, they lose an iodine atom to become T3. The conversion from T4 to T3 sends healthy messages to other cells in the body; this process allows your body to perform some of the actions it is meant to do – convert T4 into T3 and sending messages to cells and tissues around the body.
While doctors traditionally prescribed T4 for hypothyroidism, providing a supplement of both T3 and T4 may be more beneficial for some patients. Those who have undergone a total thyroidectomy that involves removal of the entire thyroid gland may benefit from T3 and T4 supplements, for example. Furthermore, other thyroid conditions may benefit from a combination of T3, T4, and other compounds.
Compounded Thyroid Medication
Pharmacies stock large amounts of certain medications to treat common problems. A pharmacy might have hundreds of patients with high blood pressure who fill the same antihypertensive prescription, for example.
This one-size-fits-all approach to pharmaceuticals may not work as well for patients with hypothyroidism or other thyroid diseases. Compounding pharmacies can create thyroid hormone replacement therapy that is not readily available.
When thyroid glands malfunction, they rarely stop producing hormones completely. In most cases, the thyroid gland is merely producing the wrong level of hormones. This means a doctor must order tests to measure each patient’s hormone production and determine how to make up the difference by reducing or increasing the levels of hormones. To make treatment even more complex, the hormone levels can fluctuate.
Some patients can take a widely available commercial prescription hormone supplement containing synthetic T4 and/or T3, but it only works if hormone levels never fluctuate. Many patients have hormone levels that fluctuate frequently and need to be able to alter their thyroid hormone treatment.
Compounding pharmacies create a bioidentical form of thyroid hormone replacement drugs tailored to fit the personal needs of each patient. Bioidentical thyroid medications have the same chemical structure as natural hormones.
A compounding pharmacist can compound thyroid medications to specific strengths and hormone ratios for each patient. These pharmacists can also provide personalized bioidentical forms of T3 and T4, which are easy to adjust when the results of blood tests dictate a change in levels of thyroid hormone dosages. The compounding pharmacy keeps track of the patient’s targeted formula and adjusts it according to the most current blood testing results, such as levels of TSH. This helps them make thyroid replacement therapy with bioidentical thyroid hormones safe and effective for each patient. Close monitoring also helps patients avoid side effects, such as weight gain, blurred vision, and tiredness.
Compounded Thyroid Medication
Compounded thyroid medication for underactive thyroid hormone may include:
- Compounded capsules available in strengths from ¼ grain (15mg) up to 5 grain (300mg)
- Natural selenium and iodine supplements that enhance thyroid hormone uptake and conversion reactions from T4 to T3
- BioIdentical T3/T4 formulations in immediate-release and sustained-release formulations
- Natural Desiccated Thyroid USP formulations, also known as thyroid extract
Compounding pharmacies can customize dosages and fillers to meet every patient’s unique needs. Many patients and prescribers request dye-free and lactose-free formulations. Compounding pharmacies may also offer vegetable capsules for those patients who wish to avoid gelatin.
Learn More About Thyroid Hormone Replacement
For more information on how compounding pharmacies can aid in thyroid hormone replacement, contact Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy, LLC. Our compounding pharmacists are eager to provide personalized compounding for your individual thyroid hormone replacement needs.