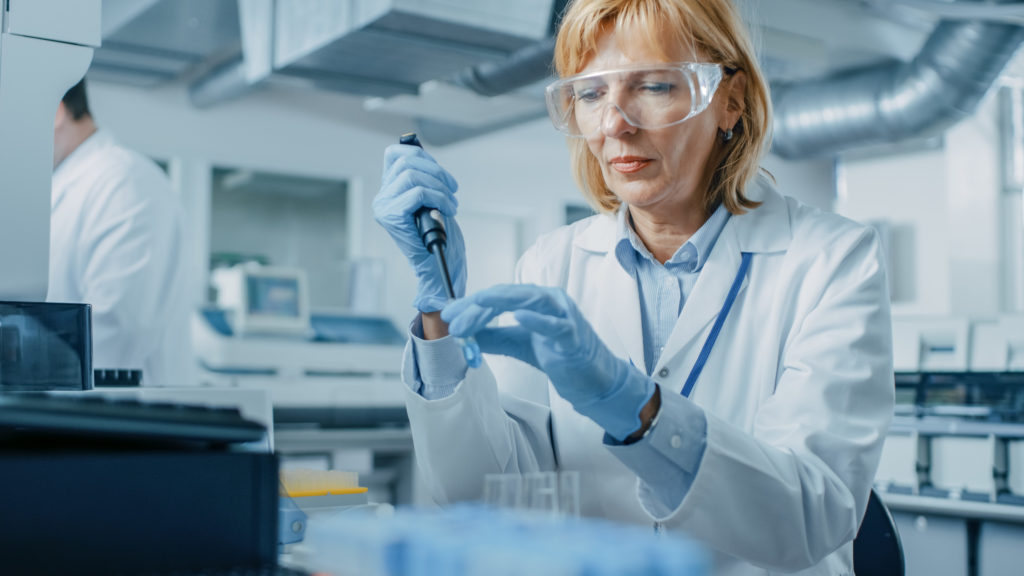
An estimated 39 million people in the United States visited a dermatologist in 2010, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Dermatologists provided or prescribed medicine at 66 percent of these office visits. Every patient who visits a dermatologist has unique needs; compounding drugs can help dermatologists meet these needs.
Dermatologists diagnose and treat more than 3,000 skin conditions, including skin cancer, contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, poison ivy, and other skin diseases. They can also provide support for cosmetic issues, and help patients revitalize the appearance of their skin, hair, and nails. Treatment for a skin condition and other dermatological problems often includes prescription medications. Some patients may need more than one medication. Other patients have allergies or sensitive skin and therefore need to avoid certain drugs.
Traditional drug manufacturing takes a one-size-fits-all approach. While this is a convenient and efficient way to make prescription drugs, it may not produce the results an individual patient needs. A dermatology compounding pharmacy can make these prescription medications to fit the needs of each individual, while still meeting the same high-quality standards required by state boards of pharmacy.
Benefits of Pharmaceutical Compounding for Dermatology Drugs
A medication’s base plays a major role in the overall effectiveness of a dermatology drug. An ointment base may increase the potency of certain steroids, for example. The base of a medication can also affect the evaporation of water out of the skin, either to dry a patch of skin out or to cause the skin to retain moisture.
Pharmaceutical compounding is a powerful and effective tool for skincare and skin treatments. When tailored specifically to meet an individual patient’s needs, skin medications may be better absorbed by the body. This means more medicine gets into the deeper layers of skin, where it can go to work to treat the problem. After all, drugs can only work if they reach the cells and tissues in need of treatment.
Compounding pharmacists can prepare dermatological medications without unnecessary additives or preservatives for patients with allergies. These specially blended compound medications can also minimize the risk of some side effects or adverse reactions.
A compounding pharmacy can combine multiple active ingredients into a single medication. For example, compounding pharmacists can combine an anti-inflammatory, anti-fungal, and pain-relieving anesthetic into a single compatible application that does three things. They can also incorporate non-prescription ingredients into a compounded drug to improve effects, such as adding sunscreen to reduce reactions to sunlight and moisturizers to treat dry skin.
Compounding pharmacists can also create topical medications in different dosage forms, such as topical creams, ointments, gels, solutions, and lotions, to make them easier or more convenient to use.
Common Dermatological Conditions and their Treatments
Compounded dermatological medications can treat a wide variety of simple and serious skin conditions. Dermatology compounding can create aesthetic treatments that reduce the number of visible age spots, diminish the appearance of wrinkles, and reactivate hair follicles to reverse balding.
A number of compounded medications are available in a variety of dosage forms to treat common dermatological conditions.
Conditions treated with compounded dermatological preparations include:
- Acne
- Alopecia
- Dry, cracking skin
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Rashes
- Rosacea
- Skin cancer
- Warts
- Wounds
- Scars
Medications used to treat dermatological conditions include:
- Acne Preparations (Topical)
- Azelaic Acid
- Adapalene, Isotretinoin, Tretinoin (Topical)
- Antifungal (Oral)
- Antifungal Preparations(Topical)
- Antihistamines (Oral)
- Cephalosporins (Oral)
- Emulsifying Ointment
- Erythromycin
- Hydroquinone
- Isoretinoin (Oral)
- Methotrexate (Oral)
- Methoxsalen Lotion (Topical)
- Minoxidil (Topical)
- Penicillins (Oral)
- Potassium Permanganate
- Steroids (Oral)
- Steroids (Topical)
- Sunscreens
- Tetracyclines
Some of these medications work by suppressing the immune system to treat severe cases of psoriasis and eczema. Antifungals treat fungal infections of the nails, antibiotics treat skin infections, antiviral agents treat herpes and shingles, and corticosteroids treat eczema. A dermatologist might recommend biologics or retinoids to treat psoriasis, benzoyl peroxide for acne, and prescribe enzyme inhibitors for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis/eczema.
Dermatological Compounding and You
While active ingredients cause predictable therapeutic effects, the outcome of dermatological treatment can vary widely, due to differences in physiology, ease of administration, and the amount of active and inactive ingredients absorbed by the human body.
Compounding pharmacists can work with you and your dermatologist to determine the best method of administration for you. Compounding dermatological products is a personalized service that can improve the outcome of treatment. Together, you and your dermatological treatment team can maximize the potential for positive outcomes using a systemized and personalized approach to treatment.
For more information on why pharmaceutical compounding is great for dermatological conditions, contact Pavilion Compounding Pharmacy today.